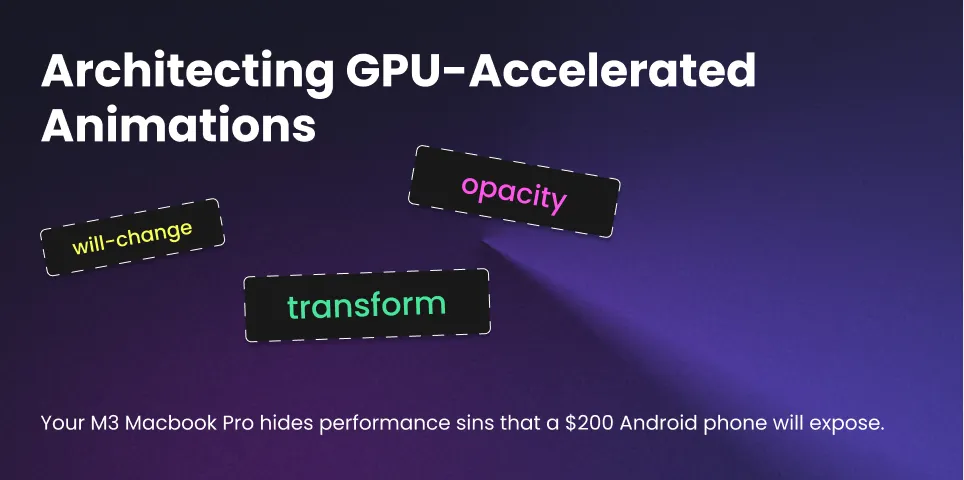
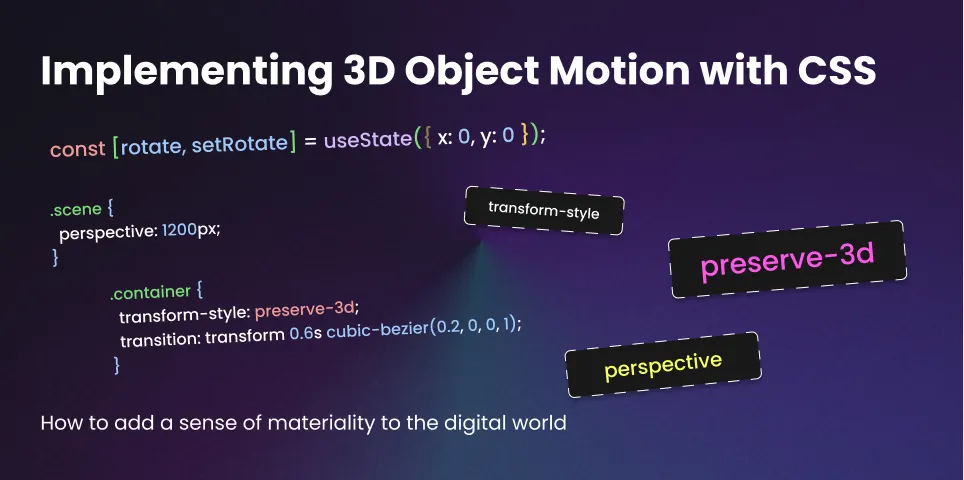
The Solution
body {
accent-color: #ff4500; /* Your Brand Color */
}Why it works: This one line tints all native form controls (checkboxes, radios, progress bars, sliders) to your specific brand color while keeping the native browser accessibility and UI fidelity intact.